KAIST AI 대학원 신기정 교수님의 수업인 데이터마이닝 및 소셜 네트워크 분석 수업 필기입니다.
Graph Machine Learning Tasks
- Node classification: Predict the property of a node
- Link Prediction: Predict how networks evolve, Predict whether there are missing links between two nodes
- Graph classification: Categorize different graphs
- Clustering: Identify densely linked clusters of nodes
- Ranking: Measure importance of nodes
- Many others+
Graphs (or Networks)

- \(V\): set of nodes (or vertices)
- \(E\): set of edges (or links)
Type of Graphs
- Undirected networks: Edges without directions
- directed networks: Edges with directions

- Unweighted networks: Edges without numbers
- Weighted networks: Edges with numbers
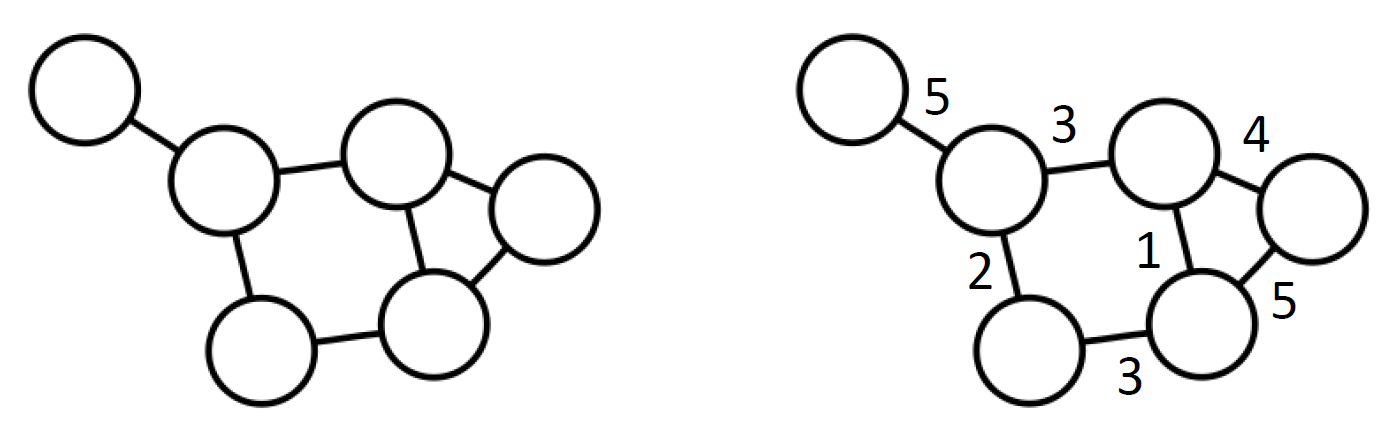
- (Unipartite) networks: one type of nodes
- Bipartite networks: Two types of nodes, Only different types of nodes can be joined by edges
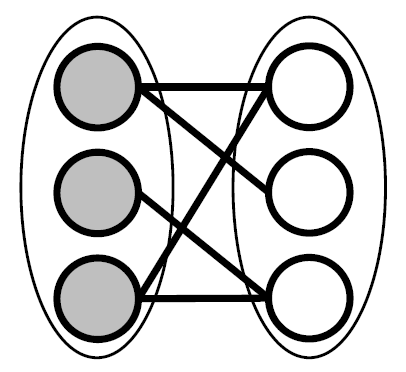
Projected / Folded Graph
Projection of a bipartite graph results in two projected graphs

Neighbors / Degree / Out and In Degree
Neighbors of node \(v\): a set of nodes adjacent to \(v\)
Degree of node \(v\): the number of neighbors of \(v\)
\(d_{out}(v)\): the number of out-going neighbors of node \(v\)
\(d_{in}(v)\): the number of in-coming neighbors of node \(v\)

- N(1) = {2,5} d(1) = 2 \(d_out(1)\) = 1 \(d_in(1)\) = 1
- N(2) = {1,3,5} d(2) = 3 \(d_out(2)\) = 1 \(d_in(2)\) = 3
- N(3) = {2,4} d(3) = 2 \(d_out(3)\) = 2 \(d_in(2)\) = 0
- ...
Representing Graphs
Edge list: set of edges, each of which is a node pair
Adjacent list: a set of neighbors for each node
Adjacency matrix \(A\) of a unipartite undirected network \(G\)
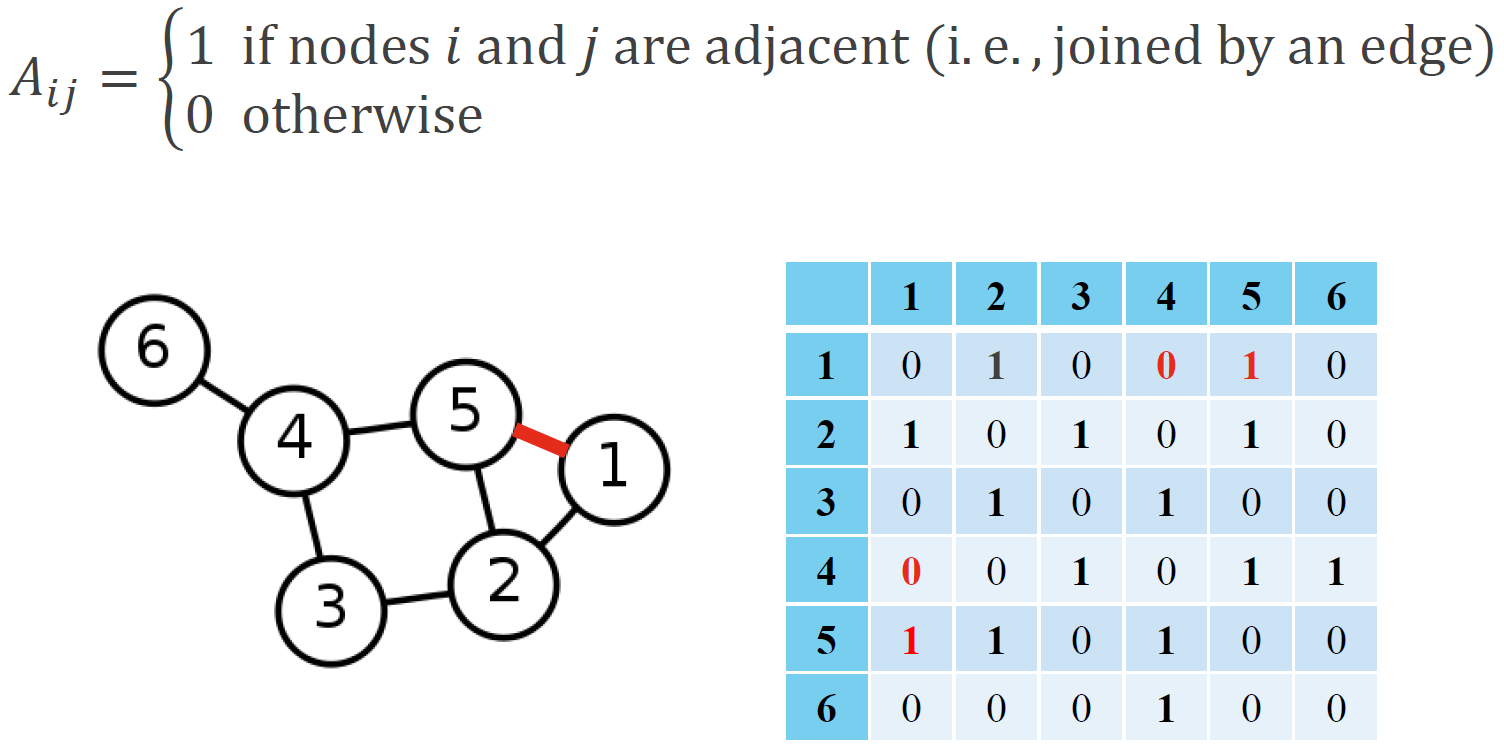
Adjacency matrix \(A\) of a unipartite directed network \(G\)

Adjacency Matrices are Spares

Most entries are zero since networks are sparse!
Use data structures and functions for sparse matrices
Connectivity of Undirected Graphs
Connected graph: Any two nodes can be joined by a path
Disconnected graph: made up by two or more connected componets

Strongly connected directed graph: a path from each node to every other node
Weakly connected directed graph: is connected if we disregard the edge directions

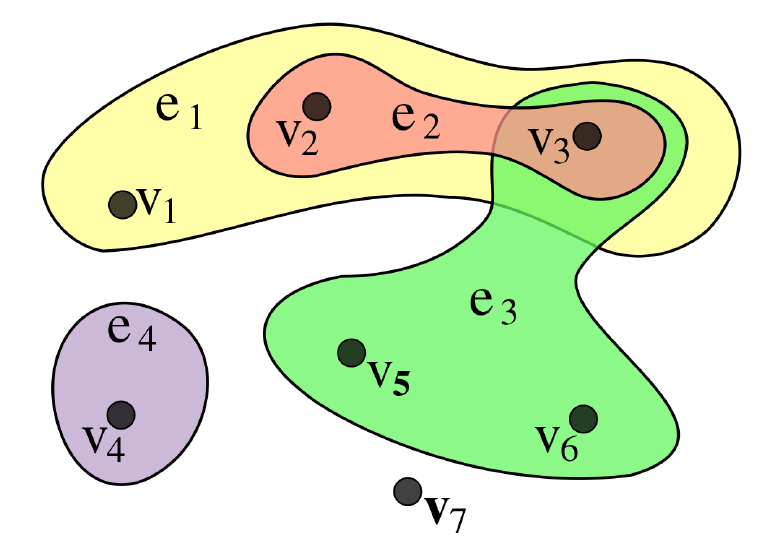
Hypergraphs
A hypergraph(or a hypernetwork) \(G\) consists of \(V\), \(H\) -> \(H\): set of hyperedges
'GraphMining' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Kronecker Graph Model (0) | 2022.09.26 |
|---|---|
| Community Guided Attachment & Forest Fire Model (0) | 2022.09.26 |
| Basic Models (0) | 2022.09.14 |
| Structural properties (2) | 2022.09.14 |
| Random Networks (0) | 2022.09.14 |
