KAIST AI 대학원 신기정 교수님의 수업인 데이터마이닝 및 소셜 네트워크 분석 수업 필기입니다.
Community Guided Attachment Model
마지막 leaf node들이 어느 Community에 속해있는지를 토대로 link probability로 edge를 생성
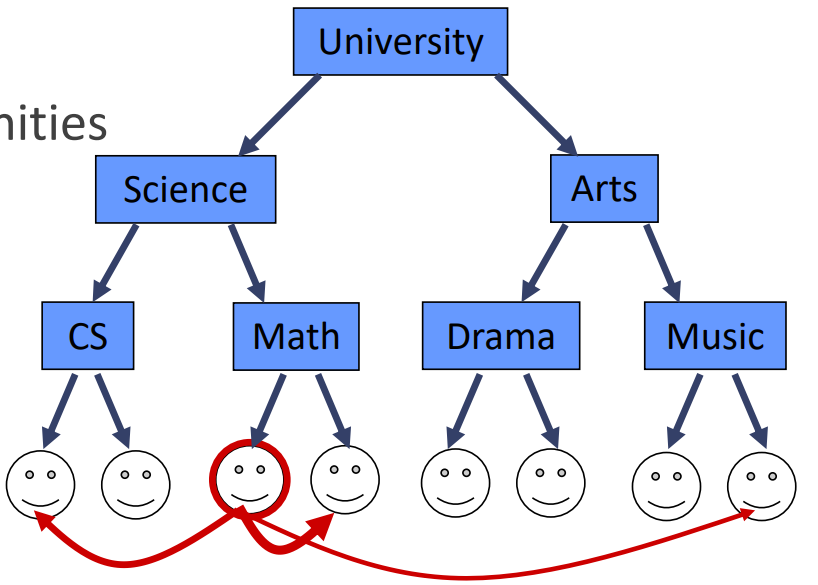
Assume
- Community structure : Group 안에는 friendship이 높고, Group 밖에는 friendship이 낮음
- Self Similarity : Perfect balanced Tree Structure
Linking probability(Difficulty Function)
$$ f(h) = c^{-h} $$
- \(h\) : tree distance of two nodes
- \(c\) : Difficulty Constant (cross-communities links become harder to form as \(c\) increases)
Densification Power Law
IF the Difficulty Function is \(f(h) = c^{-h}\), with \(1<c<b)\)
$$ a = 2 - log_b(c) $$
- \(b\) : branching factor(parent node의 number of child node)
Dynamic Community Guided Attachment Model
Community Guided Attachment과 비슷하지만 DCGA에서는 시간의 개념이 존재하여서 시간이 지남에 따라 새로운 leaf node들이 생성되고 time t에 생성된 leaf node이 자신을 제외한 모든 node들의 link probability로 edge를 생성
Assume
- Only leaf node의 out degree만 생성됨
- Self Similarity : Perfect balanced Tree Structure
Linking probability(Difficulty Function)
$$ f(h) = c^{-d(v,w)/2} $$
- when \(c < b\), the average node degree is n1−logb(c) and the in-degrees follow a Zipf distribution with exponent \({1\over2}log_b(c)\)
- when \(b < c < c^2\), the average node degree is constant, and the in-degrees follow a Zipf distribution with exponent \(1-{1\over2}log_b(c)\)
- when \(c > b^2\), the average node degree is constant and the probability of an in-degree exceeding any constant bound k decreases exponentially in k
Forest Fire Model
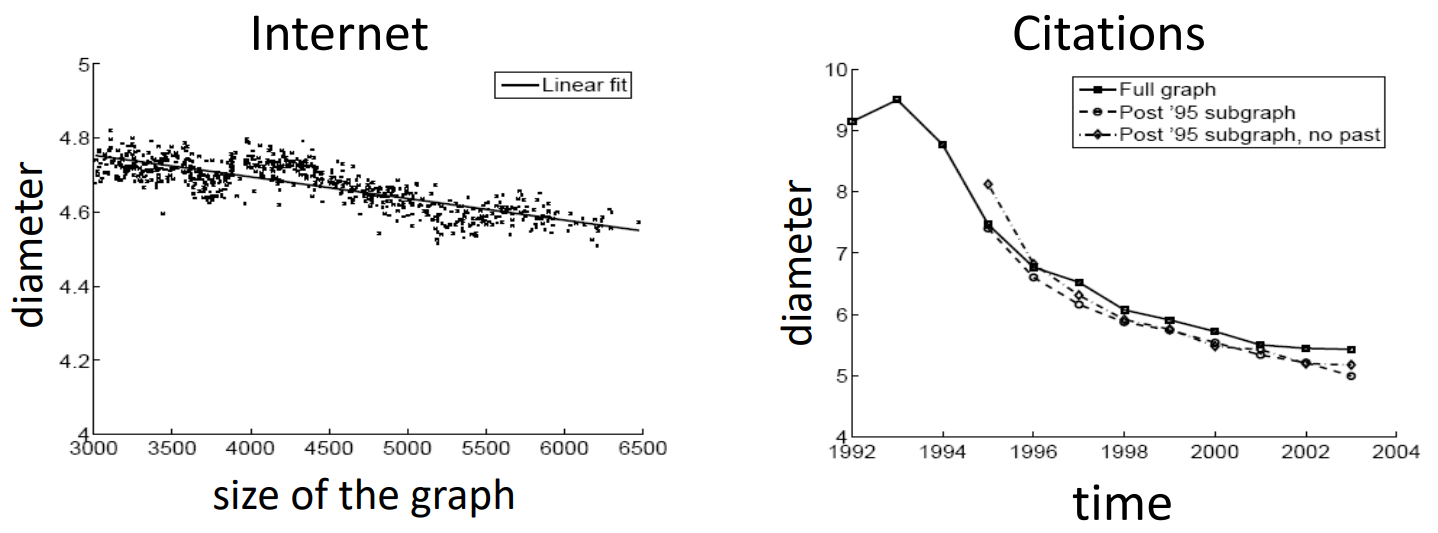
Diameter shrinks over time in Real World graph, but CGA's diameter is not shrink.
Process
\(p\) : forward burning probability
\(r\) : backward burning ratio
\(v\) : new node at time t
\(G_t\) : graph constructed
- \(v\)가 random하게 ambassador node \(w\)를 선택 후 \(v -> w\) link 생성
- Generate the number of in and out-link of \(w\) to follow (burn) -> binomial probability에 따라서
즉, \(w\)의 x개의 link를 각각 p와 rp확률로 선택하여 link를 생성
in-link binomial probability : rp / (1-rp)
out-link binomial probability : p / (1-p) - Fire spreads recursively until it dies
Property
- Why heavy-tailed in-degrees?
->rich-get-richer flavor(link가 많은 node가 점점더 link 더 많아짐) - Why heavy-tailed out-degree?
-> recursive nature of link는 new node to burn many edges and thus produce a large out-degree의 기회 제공 - Why densification&communities?
->새로운 node가 community of the ambassador와 가까우면 많은 link를 갖게 되고 멀면 적은 link를 갖게 됨 - Why shrinking diameter?
-> Unfortunately, it is not clear - Sweet spot with both densification and shrinking dimeter is very narrow
-> hyperparameter에 매우 민감(p와 r)


'GraphMining' 카테고리의 다른 글
| K-Core & Katz index (1) | 2022.10.07 |
|---|---|
| Kronecker Graph Model (0) | 2022.09.26 |
| Basic Models (0) | 2022.09.14 |
| Structural properties (2) | 2022.09.14 |
| Random Networks (0) | 2022.09.14 |
