KAIST 김재철 AI 대학원 최윤재 교수님의 수업인 인공지능을 위한 프로그래밍을 참조했습니다
Artificial Intelligence
Make machines/computers mimic human intelligence
Concept as old as the computer (Chess program by Alan Turing)
Machine Learning
Use statistical methods to teach machines to learn from data to be good at a specific task (Spam filtering)
Deep Learning
Train machines to be good at complex tasks based on neural networks and massive data
Machine Learning Categories
- Superviesd Learning: Learn a function that maps an input x to an output y
- Examples
- Image classification
- French-English translation
- Image captionng
- Examples
- Unsuperviesd Learning: Learn a distribution / manifold function of data X (no label y)
- Examples
- Clustering
- Low-rank matrix factorization
- Kernel density estimator
- Generative Models
- Examples
- Reinforcement Learning: Given an environment E and a set of actions A, learn a function that maximizes the long-term reward R
- Examples
- Go
- Atari
- Self-driving car
- Examples
Supervised Learning과 Unsuperviesd Learning의 경계는 모호하다...
Optimization
모든 모델들은 training이 필요하다(learning a function).
\(f(x; \theta)\) -> objective function(our goal)
find \(\theta\) Minimize loss(\(y\), \(f(x; \theta)\)) -> optimization
find \(\theta^*\) -> Minimize loss -> achieving objective -> successfully learning function(=training model)
반대로 진행하는 것이 우리의 방식
How to Optimize Model
Numerical method: Iteratively find a better \(\theta\) until you are satisfied
Gradient Descent: Updating parameters \(\theta\) based on training data X, Y

Stochastic Gradient Descent: Updating parameters based on a subset of the training data
Why use SGD? : data is too big, help avoid local minimum, If minibatches are I.I.D -> GD
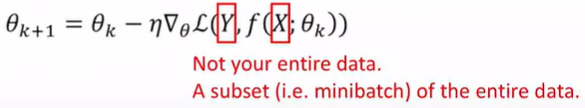
Evaluation
When we stop the traing?
- Accuracy: Used for multi-class classification
- Area under the ROC(AUROC): Used for binary classification
- Precision & Recall: Used for information retrieval
- BLEU Score: Used for machine translation
- Perplexity: Used for language modeling
- FID Score: Use for image generation
Train & Validation & Test
N-fold Cross Validation: Test model's performance in diverse train/validation/test splits

Overfitting & Underfitting
Data complexity VS model capacity

Regularization
Restrict the freedom of your model(Downsizing the hypothesis space)
\(L_1\) regularization, \(L_2\) regularization
Popular Classifiers
- Logistic Regression
- Probability -> Odds -> Log of odds (Logit)
Logit: \(ln\frac{p}{1-p}\) - Assume the logit can be modeled linearly
- Trained via gradient descent
- Probability -> Odds -> Log of odds (Logit)
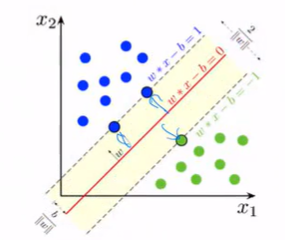
- Support Vector Machine(SVM)
- Maximize the margin between two classes
- Trained via constrained optimization (Lagrange Multiplier)
- Decision Tree
- Build a tree based on features
- Trained via the CART algorithm
- Ensembles
- Use multiple classifiers to improve performance
- Bagging
- Boosting
Popular Clustering
- K-means
- Update membership of each sample using the closest centroid
- Update the centroid value using all the member samples
- Repeat the above step
- Mixture of Gaussian
- Generalization of K-means clustering
- A sample has a probabilistic membership to each cluster
- Trained via Expectation-Maximization (EM)

